Diseases and Treatments
The prevention, recovery and preservation of your visual health is our priority.
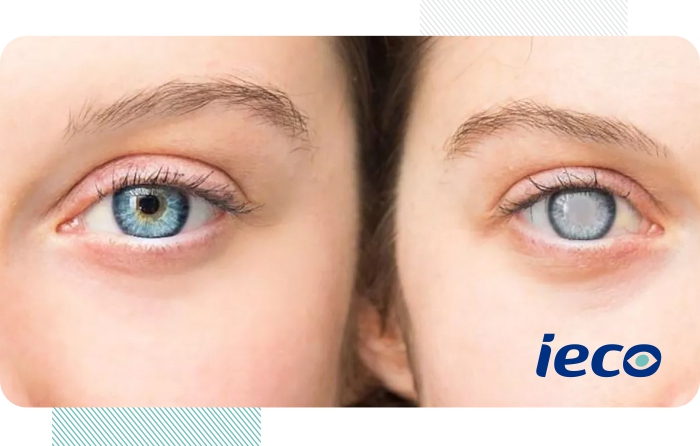
Eye cataract
Opacity of the normally clear lens of the eye. The main symptom is blurred vision.
Cataracts are an eye condition in which the lens of the eye becomes opaque, resulting in blurred or cloudy vision. It is one of the leading causes of vision loss in older people. The most common treatment for cataracts is lens replacement surgery.
Treatments
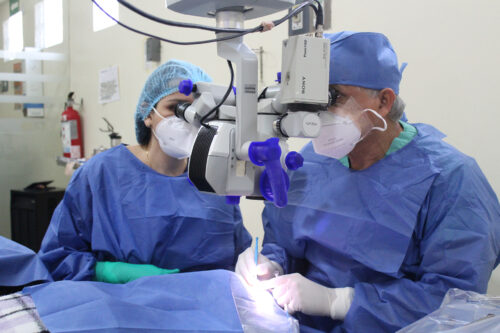
Phacoemulsification is the most modern technique for cataract management. It is performed with ultrasound equipment that vibrates at 60,000 revolutions per minute, pulverizing the cataract (emulsification).
Its great advantage over the conventional manual cataract surgery technique (extracapsular surgery) consists in using a very small incision, only 3 mm, through which the surgery is performed and the intraocular lens is implanted, which at the same time must be flexible to be able to pass through the small incision.
Another great advantage of the technique is early rehabilitation, since the patient does not require special care. Nowadays, cataract surgery with Ultrasound (Phacoemulsification) has a success rate of 99% or more, in trained hands, performed on an outpatient basis, with local topical anesthesia (drops). The average time is 10 to 15 minutes per procedure.
Myopia, Astigmatism and Hyperopia.
The myopic eye has a longer than normal length. Astigmatisms are defects that depend on the regularity (sphericity) of the optical surfaces, especially the cornea. They often coexist with myopia or hyperopia.
Treatments

Currently in Mexico, many people who have eye problems opt for laser surgery. This is due to the great results it has had in recent decades. In addition, advances in technology have allowed the development of more precise and powerful lasers, which have significantly increased the success of this surgery.
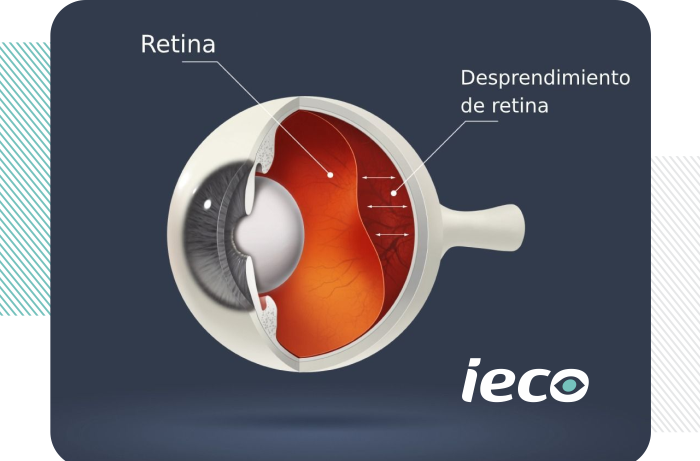
Retinal detachment
Retinal detachment consists of the separation of the sensory retina from the rest of the layers of the eyeball. When detached, this thin membrane floats inside the eye and is deprived of the nourishment it normally receives from the choroid, causing it to lose its life.
Treatments
Strabismus
Strabismus is a visual problem that occurs when the eyes are not properly aligned. It can appear from birth, childhood or during adulthood.
Its origin has different causes such as: lack of control in the muscles that are in charge of ocular motility, need for glasses, systemic diseases such as diabetes, among many other causes.
Symptoms
Commonly it can be seen with the naked eye during an ophthalmologic examination that the eyes are misaligned.
In children it may be accompanied by the need to "wink" one eye or tilt the head.
Strabismus can impair the quality and quantity of vision. This causes difficulty to see far away, learning difficulties and loss or decrease of vision in "third dimension".
When it occurs in adults it can cause "diplopia" or double vision.
Persons at risk
- Family history of strabismus.
- History of prematurity, cerebral palsy or Down syndrome.
- Siblings or parents wearing glasses with high prescriptions (nearsightedness or farsightedness)
- History of congenital cataract (cataract in children)
- Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension.
It is important to emphasize that:
EVERY CHILD SHOULD HAVE A CHECKUP BY THE OPTALMOLOGIST BEFORE THE AGE OF 4 YEARS,
to rule out visual problems.
Treatments
Depending on the age and type of strabismus present, various therapeutic approaches are considered:
- A group of patients may benefit from exclusive treatment with prescription lenses, especially in the case of children whose prescription requires specific techniques different from those used in adults.
- In other cases, the application of botulinum toxin directly to the muscles responsible for ocular motility may be necessary.
- A significant segment of patients will demand surgical intervention to achieve improved eye alignment.
- Some patients may require a combination of multiple treatments, such as surgery and prescription lenses, to achieve optimal results.
Specialties and treatments

The prevention, recovery and preservation of your visual health is our priority.